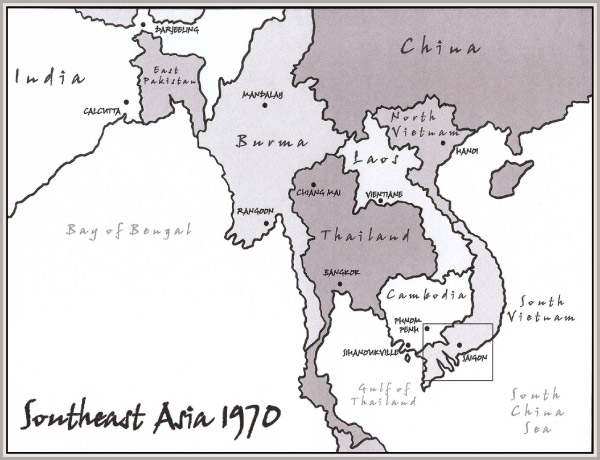
Bangkok − the capital of Thailand and its largest urban area. Located on the Chao Phraya River, it is a thriving economic center and perhaps the most important city in Southeast Asia.
Calcutta − is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal in the Ganges River delta. It is the commercial capital of eastern India and one the largest metropolitan areas in the world.
Chang Mai − located 700 km north of Bangkok, it is the largest and most culturally significant city in northern Thailand and has long been a major center for hand-crafted goods.
Darjeeling − a town in the Indian state of West Bengal, located between Sikkim, East Pakistan (now Bangladesh), and Nepal. The town dates back to the mid-19th century when the British developed it as a resort. It is famous for its locally-grown tea.
Hanoi − located 1150 km north of Saigon, it is the capital of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North Vietnam) and now the capital of the unified country.
Mandalay − the second-largest city in Burma (now Myanmar) and the one-time royal capital, located 720 km north of Rangoon on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River. It is considered the center of Burmese culture.
Phnom Penh − the capital of Cambodia, located at the intersection of the Mekong River and the Tonlé Sap and 250 northwest of Saigon. Through mid-1970 the French built capital was the only the colonial capital in Southeast Asia to be spared the effects of war and unbridled commercialization.
Rangoon (now Yangon) − founded by the British in southern Burma as a commercial and political center, the city has slowly degenerated since independence in 1948 and now is the least developed major city in Southeast Asia.
Saigon (now Ho Chi Minh City) − capital of the Republic of South Vietnam until the country was absorbed by the North Vietnamese in 1976.
Sihanoukville − a port and resort town on the Gulf of Thailand 230 km southwest of Phnom Penh. It was developed in the 1960’s as a shipping alternative to the Mekong River.
Vientiane − the relatively small administrative capital of Laos is located on the Mekong River. Founded by the French who retired in 1953, it has since weathered American, Vietnamese, Laotian communist, and Russian influences.
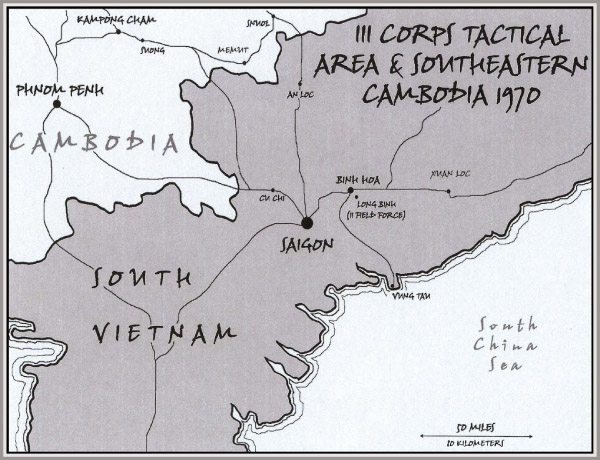
II Field Force – located adjacent to Long Binh Post, the U.S. Army corps-level command responsible for the III Corps Tactical Zone, which comprised eleven provinces surrounding Saigon
An Loc – a town 110 km north of Saigon which was the local U.S. military headquarters for the invasion of Cambodia.
Bien Hoa – a city in Dong Nai Provence, South Vietnam, 30 km northeast of Saigon and adjacent to Long Binh Post and the II Field Force compound
Cu Chi – located 35 km northwest of Saigon, the U.S. Army’s 25th Division was headquartered there. It is famous for its nearby “Cu Chi Tunnels,” an underground Viet Cong military base.
Kampong Cham – a provincial capital in Cambodia, 100 km northeast of Phnom Penh
Long Binh (Long Binh Post) – a sprawling logistics facility and the largest U.S. Army base in Vietnam, located adjacent to the II Field Force compound and adjacent to the city of Bien Hoa
Memut & Snuol – small towns just inside the Cambodian border
Phnom Penh – the capital of Cambodia
Saigon – known as the “Pearl of the Orient” during the French colonial period, it was the capital of the Republic of Vietnam until 1975 when it was overrun by the North Vietnamese and renamed “Ho Chi Minh City.”
Suong – Cambodian town 20 km east of Kampong Cham and site of the convent described in the novel
Vung Tau – a port town located on the Atlantic Coast 115 km southeast of Saigon and originally developed as a resort. It served as an in-country R & R center for U.S. military personnel.
Xuan Loc – a town 50 km east of Bien Hoa and site of the last major battle of the Vietnam War